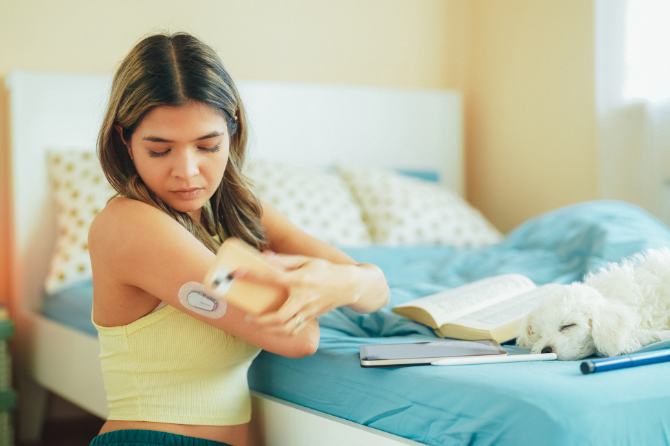

Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many misconceptions and uncertainties about the disease persist. This blog aims to shed light on some crucial aspects of T1D, from life expectancy to symptoms and treatment options, helping you understand and manage this condition effectively.
Life Expectancy of a Type 1 Diabetic
Type 1 Diabetes, once considered a fatal disease, has seen remarkable improvements in management and care over the decades. Advances in insulin therapies, monitoring technologies, and comprehensive care approaches have significantly improved the quality of life and longevity of individuals with T1D. Studies indicate that with proper management, the life expectancy of someone with Type 1 Diabetes can be close to that of the general population. More details can be found in this CDC overview on diabetes management.
Differences Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Although both are forms of diabetes, Type 1 and Type 2 differ significantly. Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2, however, is primarily a metabolic disorder associated with insulin resistance and often linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity and physical inactivity. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective management and treatment. The American Diabetes Association provides a comprehensive comparison.
Average Age for Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosis
Type 1 Diabetes is commonly diagnosed in children and young adults, with a peak incidence in individuals aged 10 to 14 years. However, it can occur at any age, making it important for parents and caregivers to recognize the early signs such as frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, and excessive thirst. The Mayo Clinic offers insights on diagnosis and early symptoms.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
The symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes can develop suddenly and include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Extreme hunger
- Unintended weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision These symptoms occur as the body lacks sufficient insulin to process glucose properly. Learn more about the symptoms from Johns Hopkins Medicine.
Treatment Options for Type 1 Diabetes
Managing Type 1 Diabetes involves multiple daily injections of insulin or the use of an insulin pump, continuous glucose monitoring, and careful dietary and activity planning. Recent advancements have also introduced artificial pancreas systems and new forms of insulin, enhancing treatment efficacy and patient convenience. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases provides detailed information on treatment options.
Conclusion
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes is crucial for effective management and maintaining a high quality of life. If you or someone you know is dealing with Type 1 Diabetes, it’s essential to seek tailored nutritional guidance. Contact our Nutrition Department at OakBend Medical Center at 281-633-4022 or visit our Nutrition and Food Services page for more information and support.
Leave a reply







Most Commented