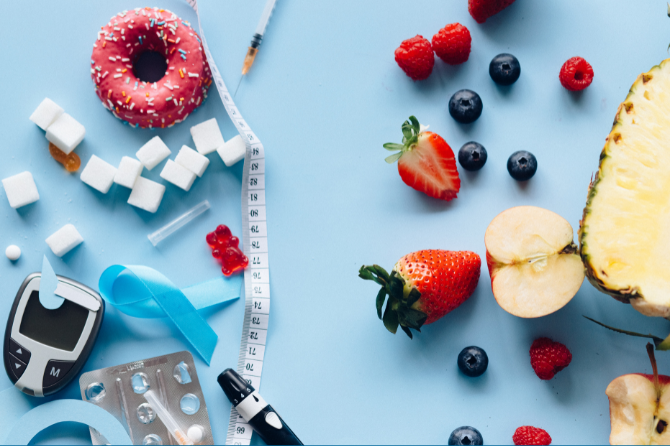
Diabetes is a condition in which blood glucose levels are above normal. When an individual suffers from diabetes, their body either does not make enough insulin (the hormone that controls glucose) or the body can’t use insulin as well as it should. Diabetes varies in severity but can cause serious health complications, including organ failure, heart disease, blindness, and lower-extremity amputations. The risk of death for adults with diabetes is five times higher than in those who do not have the disease.
Although there is no cure for diabetes, many treatments and lifestyle changes are known to manage the disease. Diabetes self-management education is the cornerstone to help individuals with diabetes manage it and achieve a better quality of life while preventing other serious complications. For more information, please contact a Houston diabetes specialist at OakBend Medical Center today.
Type 1 Diabetes (also called Juvenile-onset or insulin-dependent diabetes)
- The body does not make insulin on its own.
- Much less common than Type 2 diabetes. Only present in about 5-10% of all diabetes cases.
- Cannot be cured or prevented. Most Type 1 diabetes develops because the immune system attacks and destroys the cells that make insulin.
- Can occur in individuals of any age.
- Treated with insulin injections two or more times per day to replace the missing insulin. Some may also use an insulin pump that automatically gives a small amount of insulin throughout the day.
- There are many episodes of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), which can cause a lightheaded and shaky feeling, confusion, heart palpitations, or anxiety.
Type 2 Diabetes (also called adult-onset or non-insulin-dependent diabetes)
- The body does not make enough insulin or the body becomes resistant to insulin.
- Far more common than Type 1 diabetes. Up to 95 percent of diabetes sufferers have Type 2 diabetes.
- Can sometimes be prevented when blood glucose levels are managed by eating healthy, working out, and sustaining a healthy weight.
- Can occur in individuals of any age.
- Treated with a healthy, balanced diet, weight loss, medications, and exercise. When these are not enough, some individuals may also require insulin injections.
- There are no episodes of low blood sugar except if the individual is taking insulin or other diabetes medications.
Although there are many differences in each type of diabetes, both can be severe and lead to other serious complications. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States and the leading cause of blindness and kidney failure. For sufferers, it is vital to work with a specialized diabetes physician or dietitian and come up with a plan to manage diabetes. Keeping blood sugar under control is the first step to fighting diabetes and living a healthy life.
Managing Diabetes on Your Own
While professional medical care and guidance are essential for effectively managing diabetes, there are several steps individuals can take to proactively control their condition and improve their quality of life. Here are some key strategies for self-management:
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly checking your blood sugar levels is crucial. Your healthcare provider can guide you on how often to monitor and help you set target ranges.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Adopt a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit the intake of sugary and processed foods, as well as excessive carbohydrates.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week.
- Medication Management: If prescribed, take your diabetes medications as directed by your healthcare professional. Adhering to your medication schedule is vital for keeping your condition under control.
- Stress Management: High stress levels can affect blood sugar. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing into your daily routine.
- Healthy Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can improve insulin sensitivity. Your healthcare provider can help you set weight goals.
- Regular Eye and Foot Exams: Regular eye and foot examinations are essential for detecting and preventing diabetes-related complications.
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself about diabetes and its management. Attend diabetes education classes or workshops to learn more about the condition and how to take care of yourself.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Make necessary lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption, to reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Seek Support: Connect with support groups or online communities for individuals with diabetes. Sharing experiences and advice can be empowering and comforting.
Remember, self-management is a vital complement to the care you receive from healthcare professionals. Always consult your healthcare provider to create a personalized diabetes management plan that suits your specific needs and circumstances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetes is a serious condition that requires comprehensive management, but it’s a battle that can be won with the right strategies in place. By understanding the differences between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes and actively engaging in self-management, individuals can take charge of their health and work towards a brighter, healthier future.
If you have diabetes or pre-diabetes, please contact a Houston registered dietitian to schedule an outpatient appointment by calling 281-633-4022. The registered dietitians at OakBend offer individualized nutritional counseling for many medical conditions, including diabetes/pre-diabetes, cancer, heart disease, high blood pressure, PCOS, kidney disease, HIV/AIDS, Inflammatory bowel disease, digestive disorders, and weight management. The outpatient diabetes self-management education offered at OakBend is for both adults and children with diabetes and teaches them the skills necessary to take the best care of themselves and live healthy, active long lives.
Leave a reply