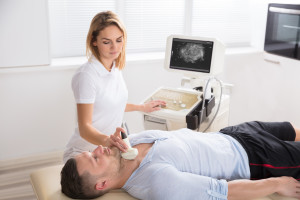
 Ultrasounds are non-invasive diagnostic exams performed to assess the organs or structures within the body. Ultrasounds use high-frequency sound waves which echo off the tissue being examined and the recorded sounds are used to create an image. Ultrasounds are safe and painless. Unlike X-ray imaging, ultrasounds do not involve any ionizing radiation exposure.
Ultrasounds are non-invasive diagnostic exams performed to assess the organs or structures within the body. Ultrasounds use high-frequency sound waves which echo off the tissue being examined and the recorded sounds are used to create an image. Ultrasounds are safe and painless. Unlike X-ray imaging, ultrasounds do not involve any ionizing radiation exposure.
Ultrasounds are most commonly used to check fetal development during pregnancy and have many other clinical uses. Physicians may order ultrasounds if a person is experiencing pain, swelling, or other abnormalities that require an internal view of the organs.
Different Types of Ultrasound Imaging:
Doppler Ultrasounds – Doppler ultrasounds measure speed and direction of blood cells as they move through the body. Doppler ultrasounds can help doctors view blockages, clots and narrowing of the blood vessels which may be caused by plaque.
Bone Sonography – Bone sonography creates images of the bones which can be used to assess bone fragility and help diagnose osteoporosis.
Echocardiograms – These ultrasounds create images of the heart and its surrounding valves.
3D and 4D Ultrasounds – 3D ultrasounds create three-dimensional interpretations instead of the flat two-dimensional images with traditional ultrasounds. 4D ultrasounds create 3D images, but in motion such as a heart beating.
Obstetric (Pregnancy) Ultrasounds – These ultrasounds are performed to determine a baby’s due date, sex, and view the baby’s anatomy. Ultrasounds can also determine if there are twins or multiple pregnancies and detect potential problems or complications with the uterus. Some issues that can be detected with an ultrasounds are birth defects, breech positioning, or placental issues.
Diagnostic Ultrasounds – Doctors use ultrasounds to diagnose a wide variety of conditions.
Abdomen Ultrasounds – These types of ultrasounds are used to evaluate the liver, pancreas, kidneys, gall bladder, spleen, aorta, appendix and IVC.
Chest Ultrasounds – Evaluate the lungs, trachea, esophagus, lymph nodes and heart. Ultrasounds of the heart and its valves are called echocardiograms. Chest ultrasounds are performed to quickly visualize the chest organs and structures from outside the body. They can also assess blood flow to the chest organs and identify if there is liquid in the chest cavity or lungs.
Visual Aid Ultrasounds – Ultrasounds are sometimes performed during medical procedures to help doctors guide needle placement in blood vessels or during a fine needle aspiration when a doctor removes a small piece of tissue for biopsy testing.
Therapeutic Ultrasounds – Therapeutic ultrasounds are mostly used by physical therapists or athletic trainers to treat injuries like muscle strains or runner’s knee. Sports medicine often uses ultrasound therapy for the rehabilitation of many back or joint injuries or chronic conditions. Ultrasound therapy causes vibration which can stimulate the repair of soft tissue injuries and relieve pain.
Pelvic Ultrasounds – Pelvic ultrasounds can be used to view the ovaries, cervix, vagina, fallopian tubes, uterus, testicles, prostate gland, bowels, or bladder. There are three methods for pelvic ultrasounds:
- Transabdominal – transabdominal ultrasounds are purely external. A gel is placed on the abdomen and then a handheld unit is gently moved around the stomach. The unit sends out high-energy sound waves which create a picture, called a sonogram, onto a computer or tv monitor. Transabdominal ultrasounds are used for both diagnostic and obstetric purposes.
- Transvaginal – transvaginal ultrasounds are performed to assess a woman’s ovaries, uterus, cervix, tubes and pelvic area. The ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina and sends out sound waves that reflect off of the surrounding structures. A computer receives these waves and creates images that doctors can use to help diagnose conditions such as cervical cancer.
- Transrectal – transrectal ultrasounds (TRUS) are performed to assess conditions with the prostate gland and surrounding tissues. The procedure involves the insertion of an ultrasound probe into the patient’s rectum. Then, sound waves are sent and received through the rectal wall which produce images of the prostate gland. TRUS exams can help diagnose symptoms such as difficulty urinating, investigate a nodule, detect abnormalities and determine if the prostate gland is enlarged.
OakBend Medical Center has a state-of-the-art Imaging Center which offers the latest technology in diagnostic imaging testing. OakBend also has a dedicated Women’s Imaging center specifically designed to provide a relaxing environment for imaging that is often known for being uncomfortable or painful. For added convenience, all three of our hospital campuses including Jackson Street and Williams Way in Richmond, TX and Wharton in Wharton, TX have imaging services during weekday and weekend hours.
To schedule an appointment, call our imaging department at (281) 341-2836 or use our online scheduling form. Imaging services may require a referral, so be sure to contact your health insurance provider before scheduling an appointment.
